C Structure
In C, there are cases where we need to store multiple attributes of an entity. It is not necessary that an entity has all the information of one type only. It can have different attributes of different data types. For example, an entity Student may have its name (string), roll number (int), marks (float). To store such type of information regarding an entity student, we have the following approaches:
- Construct individual arrays for storing names, roll numbers, and marks.
- Use a special data structure to store the collection of different data types.
Let's look at the first approach in detail.
Output
Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student 1Arun 90 91 Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student 2Varun 91 56 Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student 3Sham 89 69 Printing the Student details... Arun 90 91.000000 Varun 91 56.000000 Sham 89 69.000000
What is Structure
Structure in c is a user-defined data type that enables us to store the collection of different data types. Each element of a structure is called a member. Structures ca; simulate the use of classes and templates as it can store various information
The ,struct keyword is used to define the structure. Let's see the syntax to define the structure in c.
Let's see the example to define a structure for an entity employee in c.
The following image shows the memory allocation of the structure employee that is defined in the above example.
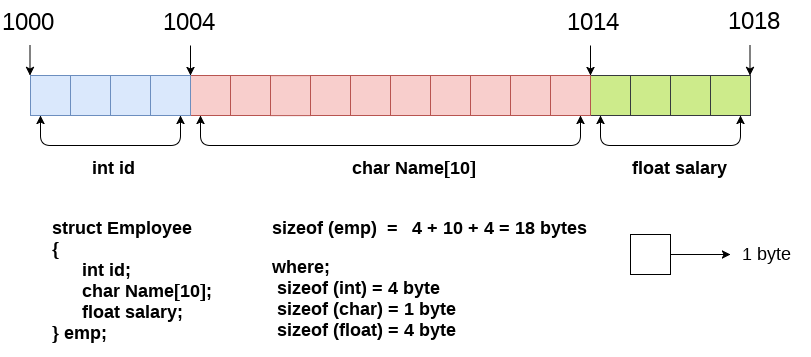
Here, struct is the keyword; employee is the name of the structure; id, name, and salary are the members or fields of the structure. Let's understand it by the diagram given below:

Declaring structure variable
We can declare a variable for the structure so that we can access the member of the structure easily. There are two ways to declare structure variable:
- By struct keyword within main() function
- By declaring a variable at the time of defining the structure.
C Structure example
Let's see a simple example of structure in C language.
Output:
employee 1 id : 101 employee 1 name : Sonoo Jaiswal
Let's see another example of the structure in C language to store many employees information.
Output:
employee 1 id : 101 employee 1 name : Sonoo Jaiswal employee 1 salary : 56000.000000 employee 2 id : 102 employee 2 name : James Bond employee 2 salary : 126000.000000