C Pointers
The pointer in C language is a variable which stores the address of another variable. This variable can be of type int, char, array, function, or any other pointer. The size of the pointer depends on the architecture. However, in 32-bit architecture the size of a pointer is 2 byte.
Consider the following example to define a pointer which stores the address of an integer.
Declaring a pointer
The pointer in c language can be declared using * (asterisk symbol). It is also known as indirection pointer used to dereference a pointer.
Pointer Example
An example of using pointers to print the address and value is given below.
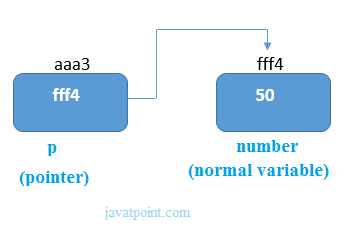
As you can see in the above figure, pointer variable stores the address of number variable, i.e., fff4. The value of number variable is 50. But the address of pointer variable p is aaa3.
By the help of * (indirection operator), we can print the value of pointer variable p.
Let's see the pointer example as explained for the above figure.
Output
Address of number variable is fff4 Address of p variable is fff4 Value of p variable is 50